From Bloating to Breathlessness: A Guide to Abdominophrenic Dyssynergia
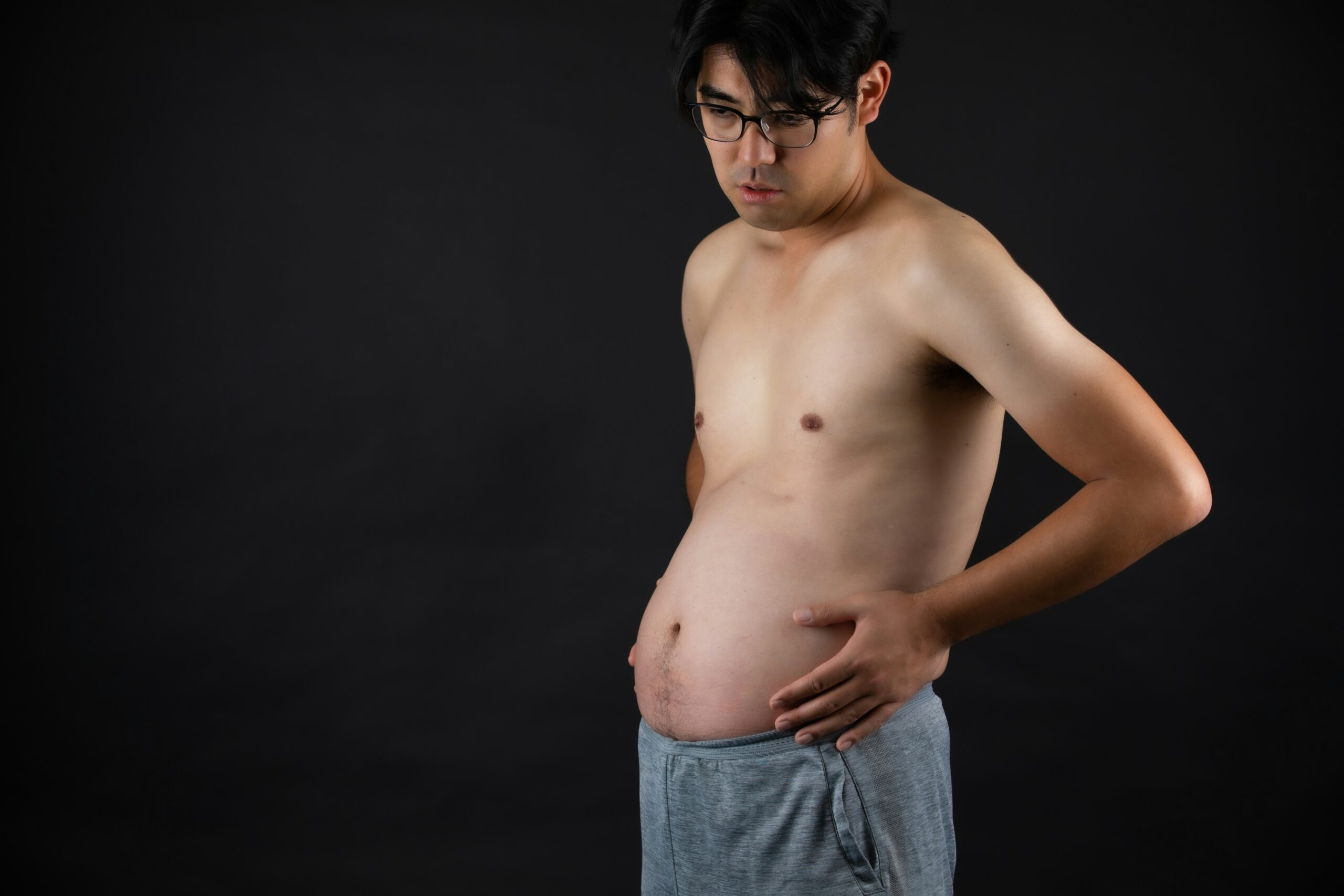
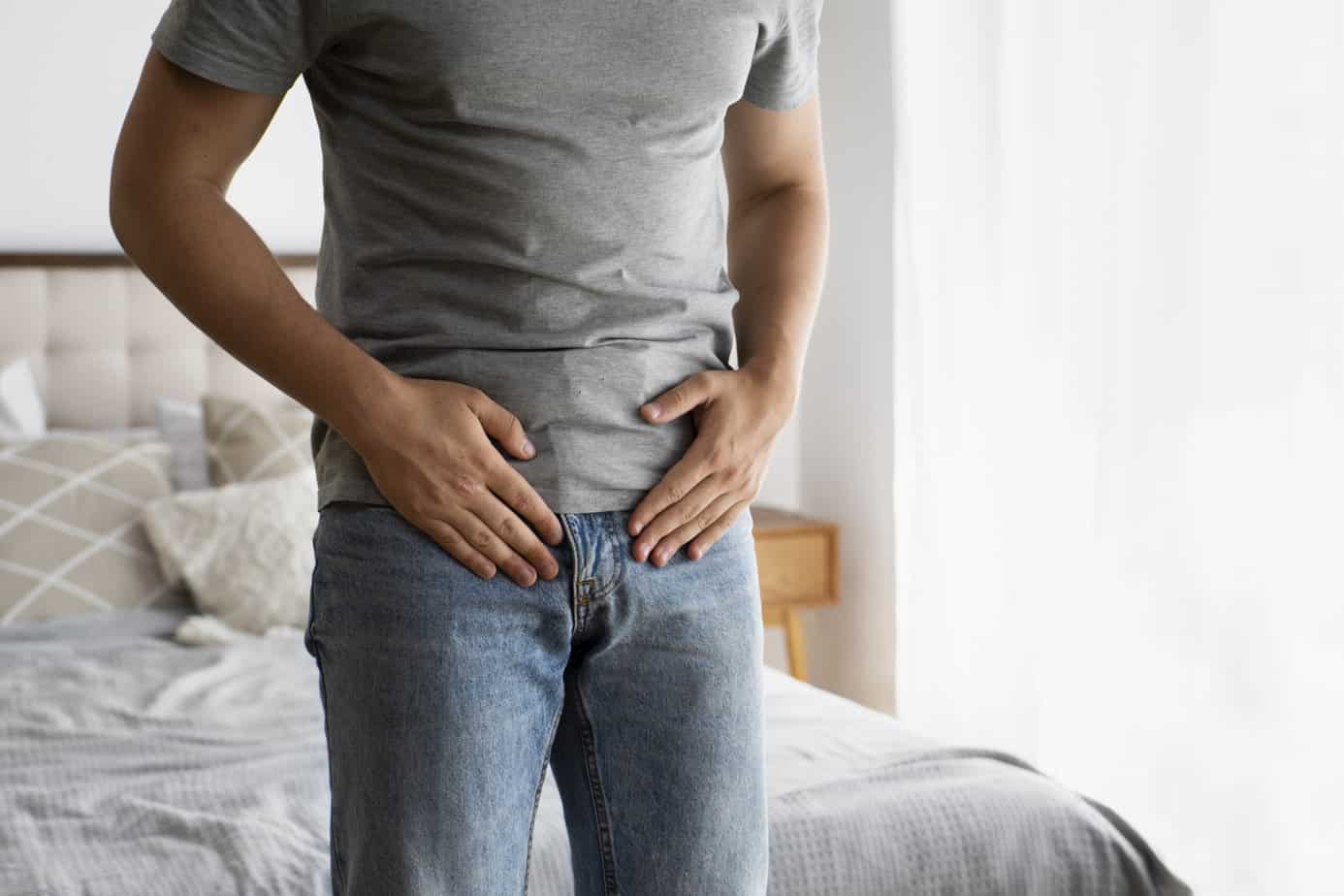
If you’ve ever looked at the above image and felt an uncomfortable familiarity—accompanied by bloating, abdominal distention, shortness of breath, or digestive troubles—then you’re in the right place. This blog is dedicated to unraveling the mystery of abdominophrenic dyssynergia, a condition that might be the key to understanding your symptoms.
What Is Abdominophrenic Dyssynergia?
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia is a condition characterized by a lack of coordination between the abdominal wall and the respiratory diaphragm. Essentially, it’s a discord between two crucial components of our breathing and digestive processes: the abdominal muscles and the diaphragm.
Who Is Affected?
This condition can impact both men and women and is often associated with several other health concerns, including:
- Diastasis Recti: A separation of the abdominal muscles, common during and after pregnancy.
- Postpartum Changes: Changes following childbirth that affect core stability.
- Gut Disorders: Conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
- Pelvic Floor Dysfunction: Issues with the muscles and connective tissues of the pelvic floor.
Why Does This Happen?
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia occurs due to a disruption in the viscerosomatic reflex. This reflex normally responds to gaseous distention in the GI tract, which happens after eating. Ideally, the abdominal wall muscles contract to manage this gas, but when this reflex is impaired, the abdominal muscles relax while the diaphragm contracts and drops lower. This abnormal response can lead to:
- Shortness of Breath: As the diaphragm lowers, it restricts the lungs’ ability to expand fully.
- Increased Abdominal Distention: As gas accumulates and the abdominal muscles fail to respond correctly.
- Digestive Issues: Prolonged abnormalities can disrupt normal digestive processes.
What Can You Do About It?
Managing abdominophrenic dyssynergia involves several strategies aimed at restoring balance and improving coordination between the diaphragm and abdominal muscles:
- Retrain the Respiratory Diaphragm: Engage in exercises to enhance the diaphragm’s mobility and coordination.
- Improve Trunk Rotation: This can help in balancing the movement and function of the abdominal and respiratory muscles.
- Enhance Rib Mobility: Flexibility in the rib cage can contribute to better breathing mechanics.
- Avoid Forward Leaning During Meals: Maintain an upright posture to support optimal digestion.
- Relax the Belly Passively: Gentle relaxation techniques can ease tension in the abdominal area.
What Should You Avoid?
To prevent exacerbating symptoms, steer clear of:
- Belly Breathing: This type of breathing can aggravate the imbalance between the diaphragm and abdominal muscles.
- Excessive Consumption of Insoluble Fiber: High amounts of insoluble fiber can increase gas production and abdominal discomfort.
By understanding and addressing abdominophrenic dyssynergia, you can take proactive steps to alleviate your symptoms and improve your overall well-being. If you suspect you have this condition, consider consulting Body Harmony Physical Therapy for personalized advice and treatment options.